Industrial Die Cutting Machines: A Complete Guide to Types, Automation, and Selection Strategies
Industrial die cutting machines are manufacturing systems used to cut and shape materials with high precision and repeatability. Common types include flatbed, rotary, and laser die cutting machines, each suited to different materials and production volumes. Automatic die cutting machines integrate features such as servo control, CCD positioning, and automatic feeding to improve efficiency and consistency. Among these options, flatbed die cutting machines remain essential for industrial applications involving thick, rigid, or multi-layer materials where cutting force and accuracy are critical.
What Is an Industrial Die Cutting Machine?
In the world of precision manufacturing, efficiency and accuracy are paramount. Unlike craft or manual die cutters, an industrial die cutting machine is engineered for continuous operation, high precision, and integration into automated production lines. These systems are designed to cut, shape, or punch materials under controlled pressure for mass manufacturing.
They are widely used across industries such as electronics, packaging, automotive components, footwear, medical supplies, and industrial materials processing, where consistency, efficiency, and scalability are critical.
Types of Industrial Die Cutting Machines
Selecting the right equipment starts with understanding the landscape of available technology. Industrial die cutting machines can be broadly categorized by their cutting mechanism and production format. Understanding these differences is essential for correct machine selection.
Flatbed Die Cutting Machine (Flatbed Die Cutter)
The most versatile and robust option in the industry is the flatbed system. A flatbed die cutting machine, also commonly referred to as a flatbed die cutter, uses a vertical press motion where the die and material remain stationary during each cutting cycle.
Flatbed systems are especially valued in industrial environments because they:
- Apply uniform cutting pressure across the entire die
- Handle thicker or multi-layer materials
- Maintain high cutting accuracy even at lower production speeds
Flatbed die cutting machines are frequently used for plastic sheets, rubber, foam, gaskets, insulation materials, and precision components, making them a cornerstone of industrial die cutting.
For instance, the common household scouring pads from brands like 3M are manufactured using hydraulic flatbed die cutting machines. Yicheen’s machines are capable of die cutting over 100 blocks simultaneously in a single cycle. Our expertise in this sector is reflected in our 80% market share within the foam and scouring pad processing industry.
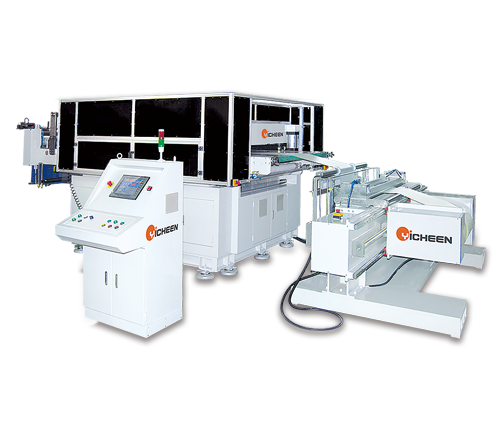

(High Precision Die Cutting Machine with CCD auto position system)

Rotary Die Cutting Machine
While flatbed machines prioritize pressure and thickness, rotary systems are built for speed. Rotary die cutting machines operate using cylindrical dies in a continuous rolling motion. They are optimized for:
- High-speed, high-volume production
- Roll-fed materials
- Thin and flexible substrates
Rotary systems excel in label production, tapes, and film processing but are less suitable for thick or rigid materials due to pressure limitations.
Laser Die Cutting Systems
Moving away from physical blades entirely, laser technology offers a digital alternative. Laser die cutting systems replace physical dies with digitally controlled laser beams. These systems offer:
- Tool-free cutting
- Extreme design flexibility
- Rapid changeovers for short runs
However, laser systems typically trade cutting force for flexibility, making them more suitable for thin materials, prototypes, or highly customized production rather than heavy-duty industrial cutting.
Digital Knife Cutting Machines (Oscillating Knife)
For materials that are sensitive to heat or require cleaner edges than lasers can provide, digital knife systems are the ideal solution. These machines use a high-frequency vibrating blade (oscillating knife) to slice through materials like heavy foam, honeycomb board, and leather without burning. Like laser systems, they are tool-free and CAD-driven, making them perfect for prototyping and short-run production.
Comparative Analysis: Flatbed vs. Rotary vs. Digital Cutting Technologies
Choosing between these technologies involves balancing material constraints with production goals and budget. There is no single "best" machine; only the right machine for a specific application.
For instance, while rotary systems offer unmatched speed, their high tooling costs make them inefficient for short runs. Conversely, laser and digital knife systems offer incredible flexibility but may struggle with the throughput required for mass production of thick parts.
The following table breaks down the critical trade-offs to help you evaluate the best fit for your production line:
| Feature / Metric | Flatbed Die Cutting | Rotary Die Cutting | Laser Die Cutting | Digital Knife (Oscillating) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Cutting Mechanism | Vertical Hydraulic Press | Continuous Rolling Cylinder | Thermal Laser Beam | High-Frequency Vibrating Blade |
| Best for Production Volume | Medium to High | Ultra-High (Mass Production) | Low / Prototyping / Custom | Low to Medium / Prototyping |
| Material Feed Format | Sheets or Roll-fed | Roll-fed only (Web) | Sheets or Roll-fed | Primarily Sheets |
| Max. Material Thickness | Excellent (Thickest & Rigid) | Limited (Thin/Flexible) | Limited (Depends on power) | Very Good (Thick Foam/Soft) |
| Cutting Force (Tonnage) | Very High | Low to Medium | N/A (Non-contact) | N/A (Slicing action) |
| Tooling (Die) Cost | Moderate (Steel rule dies) | High (Precision machined cylinders) | Zero (Digital file) | Zero (Digital file) |
| Setup & Changeover Time | Moderate | Long | Very Short (Instant) | Very Short (Instant) |
| Cut Edge Quality | Excellent (Compression cut) | Excellent (Clean slice) | Potential Burn/Melt marks | Excellent (Clean slice, no burns) |
This comparison highlights why, despite advances in digital and high-speed rotary technologies, Flatbed Die Cutting Machines remain essential for industrial applications requiring high force, versatility with thick materials, and cost-effective tooling for medium-volume runs
What Makes a Die Cutting Machine “Automatic”?
Modern manufacturing demands more than just mechanical cutting power; it requires intelligent operation. An automatic die cutting machine is defined not simply by motorization, but by its ability to perform multiple production steps with minimal human intervention.
Key automation features include:
- Automatic feeding and unloading
- Servo-driven motion control
- CCD visual positioning systems
- Inline alignment and stacking
- PLC-based process control
Automation Levels Explained
To help manufacturers assess their needs, automation can be broken down into three distinct tiers.
| Automation Level | Characteristics | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | Operator-dependent feeding and positioning | Small batch or prototyping |
| Semi-Automatic | Assisted feeding or positioning | Medium volume production |
| Fully Automatic | Integrated feeding, positioning, and discharge | High-volume industrial production |
In industrial environments, fully automatic die cutting machines significantly improve throughput, yield consistency, and labor efficiency, especially when paired with CCD positioning and servo control systems.
Power Source Matters: Hydraulic vs. Pneumatic vs. Electric
Beyond automation, the power mechanism determines the machine’s capability:
- Hydraulic: Delivers high tonnage (cutting force), essential for cutting dense rubber, thick composites, and multi-layer stacks.
- Pneumatic: Uses air pressure; faster but offers lower force, suitable for lighter materials and kiss-cutting.
- Electric (Servo): Offers the highest precision and cleaner operation, ideal for medical or electronics environments.


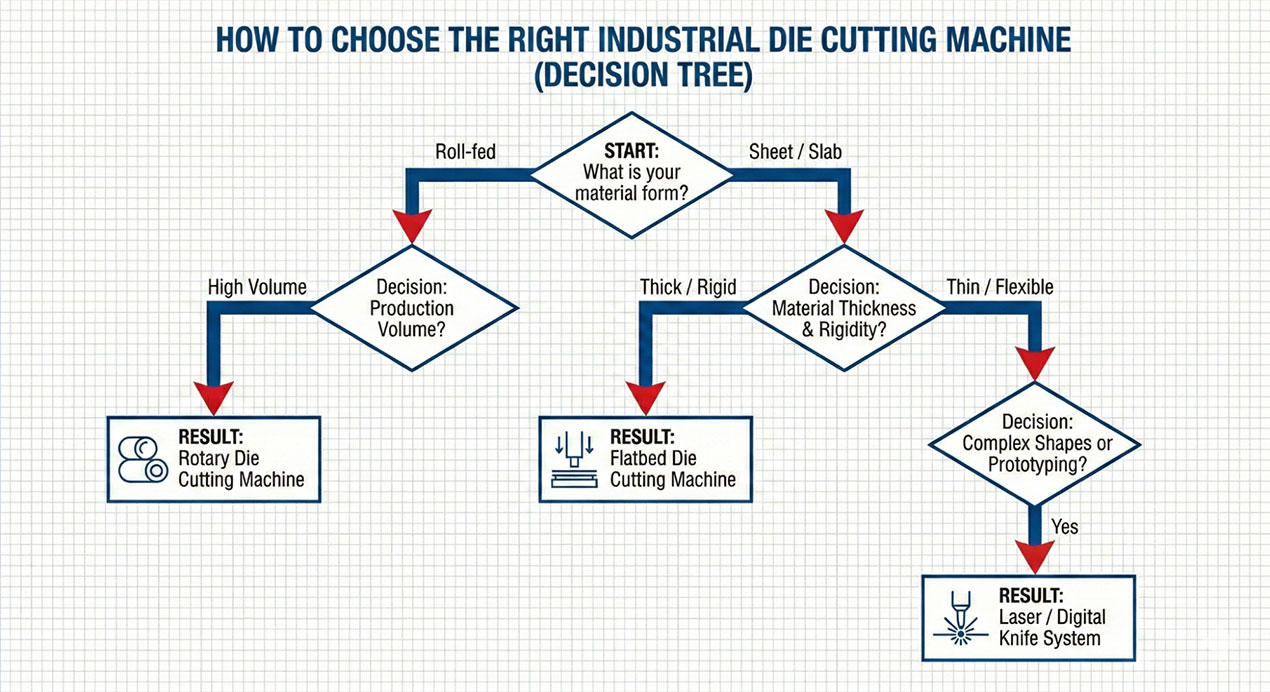
How to Choose the Right Industrial Die Cutting Machine
Making the final decision involves looking at the bigger picture of your production line. Selecting the correct industrial die cutting system requires evaluating real production conditions rather than machine specifications alone.
Key Decision Factors Checklist
- Material type (film, foam, rubber, plastic sheet, composite)
- Material thickness and density
- Required cutting force (Tonnage)
- Cutting accuracy requirements
- Production volume and cycle time
- Automation level and labor availability
- Future scalability and process integration
A machine optimized for thin film may fail with rigid sheets, while a high-pressure flatbed system may be unnecessary for ultra-high-speed roll processing. Matching machine structure to material behavior is critical.
Why Flatbed Die Cutting Machines Remain Essential in Industrial Applications
Even with the rise of alternative technologies, the traditional flatbed press has not been obsolete. Despite the availability of rotary and laser systems, flatbed die cutting machines continue to play a central role in industrial manufacturing.
Their ability to deliver consistent pressure, stable positioning, and material versatility makes them irreplaceable for applications involving:
- Thick or rigid materials
- Multi-layer cutting
- Precision industrial components
- Variable material formats
In many automated production lines, flatbed die cutting machines serve as the most reliable solution when cutting force and accuracy cannot be compromised.
Budget & ROI Considerations: New vs. Used
When planning your investment, consider the long-term value:
- New Machines: Come with warranties, the latest safety features, and technical support, ensuring long-term reliability and higher resale value.
- Used Machines: A cost-effective option for tight budgets. However, buyers should inspect the hydraulic systems and mechanical wear carefully to avoid hidden maintenance costs.
Real-World Success Story: Achieving Precision in Post-Press Blanking
To illustrate the impact of selecting the right industrial die cutting machine, consider this example from Yicheen’s portfolio.
The Challenge: Inconsistent Quality and Stacking
A printing company faced a common challenge in their post-press film blanking process. Their existing equipment was producing inconsistent cuts, resulting in messy, misaligned stacks of finished products. This not only affected product quality but also created inefficiencies in downstream packaging and handling.
The Yicheen Solution: Precision and Automation
Yicheen provided a solution focused on precision and automated handling for their post-press film blanking line. By integrating a machine with superior alignment capabilities and automated stacking features, the production process was transformed.
The Result: Perfect Alignment and Increased Efficiency
The visual comparison below speaks for itself. The materials processed by Yicheen’s equipment are perfectly aligned and neatly stacked, in stark contrast to the disorganized output from the previous equipment.
FAQs About Industrial Die Cutting Machines
Here are answers to some of the most common questions manufacturers ask when upgrading their equipment.
-
What is the difference between a flatbed die cutter and a flatbed die cutting machine?
They refer to the same industrial equipment; the difference is purely terminology.
-
Is an automatic die cutting machine always better?
Not necessarily. Automation should match production volume and material complexity. Over-automation can increase cost without improving efficiency.
-
What materials require a flatbed die cutting machine?
Materials such as rubber, foam, plastic sheets, insulation boards, and multi-layer composites typically require flatbed systems.
-
How accurate are CCD positioning die cutting machines?
CCD systems significantly improve alignment accuracy, especially for printed or patterned materials, reducing scrap and rework.
-
How do I choose between hydraulic and full-electric systems?
Hydraulic systems offer higher cutting force, while full-electric systems provide cleaner operation and faster response for precision applications.
Partner with Yicheen for Your Die Cutting Solutions
Investing in cutting technology is a strategic decision that impacts your entire production flow. Industrial die cutting machines are not one-size-fits-all solutions. Understanding machine structure, automation levels, and material behavior is the foundation of making the right investment decision.
By selecting the correct industrial, automatic, or flatbed die cutting machine, manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency, better product consistency, and long-term production stability. Ready to optimize your production line? Contact our experts for a free consultation today.